Difference between revisions of "Input-output analysis"
| (58 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Economic]] |
|||
An '''input-output model''' is a quantitative economic technique that captures inter-industry transactions. It is based on the idea that outputs from one sector in the economy become the inputs to another. For example, in order to build houses, a construction company will buy building materials from suppliers. The technique of Input-output analysis is originally created by Wassily Leontief (1965). |
|||
[[File:ae.png|25px|right|This is a page providing background in a specific field of expertise]]An '''input-output analysis''' is an estimation of the economic activities by the use of an input-output model. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Description== |
|||
| ⚫ | Based on the |
||
Industries use the products and services of other industries to produce their own products.<ref>A construction company, for instance, will buy building materials from several different suppliers, and these suppliers, in turn, will buy their inputs from suppliers further down the industry chain.</ref> An '''input-output model''' is a quantitative [[Economic tools|economic tool]] that captures these interindustry transactions. It contains large tables of data that describe the interindustry transactions in defined areas. These tables help the users to track the flow of money (in this case triggered by a development plan or existing urban object) from one industry to the next. The technique of Input-output analysis is originally created by Wassily Leontief (1966)<ref>Leontief, W.(1966): Input-Output Economics.</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
For more information about input-output analysis: |
|||
* Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Input-output_model Input-output models] |
|||
* Website: [http://www.math.psu.edu/schwede/MichiganClasses/math217/Worksheets2/leontief.pdf Pearson education. Inc] |
|||
== Relevance== |
|||
Knowledge about some frequently used economic models such as input-output models help the urban planner to systematically survey all the relevant (socio-economic) impact caused by an urban development and security threats. These insights will help the responsible urban planner to make the best choices from an socio-economic point of view. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
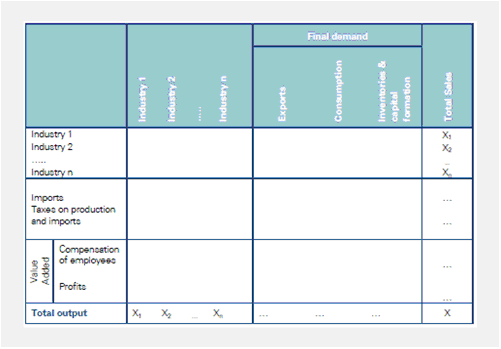
| ⚫ | Based on the [[Supporting report|supporting report]], an input-output table is created (see figure below). This table is used to calculate the infinite circulation of capital through inter-industry transactions (indirect effects) and internalizing the wages and transactions of households ([[Induced effects|induced effects]]). Since in each round capital flows out of the system (taxes, import and wages), the impact becomes gradually smaller and tends to zero in the end. This results in the so-called Leontief multipliers. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:table io analysis.png]] |
[[File:table io analysis.png]] |
||
= Multiplier effects = |
== Multiplier effects == |
||
The multiplier effect is an effect in economics "in which an increase in spending produces an increase in national income and consumption greater than the initial amount spent"<ref>Source: Dictionary.com. Online: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/multiplier+effect</ref>. For example, if a firm realises a new factory plant, it will employ construction workers and their suppliers as well as those who work in the plant. Indirectly, the new plant will stimulate employment in laundries, restaurants, and service industries in the urban environment. |
|||
The multipliers of the input-output model provide an indication of what the indirect and induced effects are of an extra unit of expenditure (the direct impact). |
The multipliers of the input-output model provide an indication of what the indirect and induced effects are of an extra unit of expenditure (the direct impact). |
||
There are two main types of multipliers: |
There are two main types of multipliers: |
||
Type I: is the multiplier of the indirect effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro leads to an additional 0.5 million euro of indirect production, the type I multiplier is 1.5; |
|||
Type II: is the multiplier of the induced effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro generates an additional consumption spending by employees of 250,000 euro, the type II multiplier is 1.25. |
|||
==Related subjects== |
|||
Urban planning processes employ a host of other economic tools/models: |
|||
* [[Social cost-benefit analysis|Social cost-benefit analysis]] |
|||
* [[Economic Impact Study|Economic impact study]] |
|||
* [[Business case|Business case]] |
|||
* [[Other economic tools|Other economic tools]] |
|||
* [[Economic tools|Economic tools]] |
|||
See also the clickable map below: |
|||
<imagemap> |
|||
Image:Economic_tools_v7.png| 350 px |
|||
rect 60 321 319 487 [[Social cost-benefit analysis|Social cost-benefit analysis]] |
|||
rect 360 550 716 763 [[Input-output analysis|Input-output analysis]] |
|||
rect 382 349 600 500 [[Economic tools|Economic tools]] |
|||
rect 289 148 456 277 [[Other economic tools|Other economic tools]] |
|||
rect 574 162 790 271 [[Business case|Business case]] |
|||
rect 978 521 1301 759 [[Economic Impact Study|Economic impact study]] |
|||
desc bottom-left |
|||
</imagemap> |
|||
Other related subjects: |
|||
* [[Economic tools]] |
|||
* [[Economic impact]] |
|||
* [[Economic dimension of urban planning]] |
|||
{{references}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 23:02, 19 January 2018
An input-output analysis is an estimation of the economic activities by the use of an input-output model.
Contents
Description
Industries use the products and services of other industries to produce their own products.[1] An input-output model is a quantitative economic tool that captures these interindustry transactions. It contains large tables of data that describe the interindustry transactions in defined areas. These tables help the users to track the flow of money (in this case triggered by a development plan or existing urban object) from one industry to the next. The technique of Input-output analysis is originally created by Wassily Leontief (1966)[2]
For more information about input-output analysis:
- Wikipedia: Input-output models
- Website: Pearson education. Inc
Relevance
Knowledge about some frequently used economic models such as input-output models help the urban planner to systematically survey all the relevant (socio-economic) impact caused by an urban development and security threats. These insights will help the responsible urban planner to make the best choices from an socio-economic point of view.
Input-output table
Based on the supporting report, an input-output table is created (see figure below). This table is used to calculate the infinite circulation of capital through inter-industry transactions (indirect effects) and internalizing the wages and transactions of households (induced effects). Since in each round capital flows out of the system (taxes, import and wages), the impact becomes gradually smaller and tends to zero in the end. This results in the so-called Leontief multipliers.
Table: Concept of an input-output model
Multiplier effects
The multiplier effect is an effect in economics "in which an increase in spending produces an increase in national income and consumption greater than the initial amount spent"[3]. For example, if a firm realises a new factory plant, it will employ construction workers and their suppliers as well as those who work in the plant. Indirectly, the new plant will stimulate employment in laundries, restaurants, and service industries in the urban environment.
The multipliers of the input-output model provide an indication of what the indirect and induced effects are of an extra unit of expenditure (the direct impact).
There are two main types of multipliers:
Type I: is the multiplier of the indirect effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro leads to an additional 0.5 million euro of indirect production, the type I multiplier is 1.5; Type II: is the multiplier of the induced effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro generates an additional consumption spending by employees of 250,000 euro, the type II multiplier is 1.25.
Related subjects
Urban planning processes employ a host of other economic tools/models:
- Social cost-benefit analysis
- Economic impact study
- Business case
- Other economic tools
- Economic tools
See also the clickable map below:
Other related subjects:
Footnotes and references
- ↑ A construction company, for instance, will buy building materials from several different suppliers, and these suppliers, in turn, will buy their inputs from suppliers further down the industry chain.
- ↑ Leontief, W.(1966): Input-Output Economics.
- ↑ Source: Dictionary.com. Online: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/multiplier+effect