Difference between revisions of "Input-output analysis"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Input/output analysis = |
|||
An '''input-output model''' is a quantitative economic technique that captures inter-industry transactions. It is based on the idea that outputs from one sector in the economy become the inputs to another. For example, in order to build houses, a construction company will buy building materials from suppliers. The technique of Input-output analysis is originally created by Wassily Leontief (1965). |
An '''input-output model''' is a quantitative economic technique that captures inter-industry transactions. It is based on the idea that outputs from one sector in the economy become the inputs to another. For example, in order to build houses, a construction company will buy building materials from suppliers. The technique of Input-output analysis is originally created by Wassily Leontief (1965). |
||
= Input-output table = |
== Input-output table == |
||
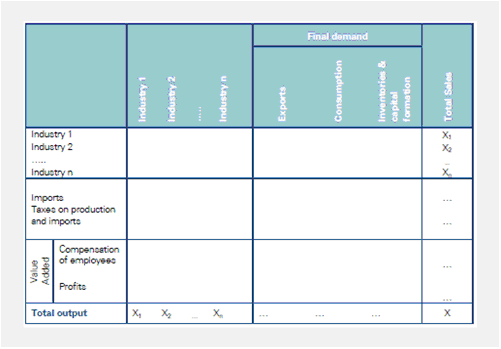
Based on the urban development plan an Input-output table is created(see figure below). This table is used to calculate the infinite circulation of capital through inter-industry transactions (indirect effects) and internalizing the wages and transactions of households (induced effects). Since in each round capital flows out of the system (taxes, import and wages), the impact becomes gradually smaller and tends to zero in the end. This results in the so-called Leontief multipliers. |
Based on the urban development plan an Input-output table is created(see figure below). This table is used to calculate the infinite circulation of capital through inter-industry transactions (indirect effects) and internalizing the wages and transactions of households (induced effects). Since in each round capital flows out of the system (taxes, import and wages), the impact becomes gradually smaller and tends to zero in the end. This results in the so-called Leontief multipliers. |
||
| Line 7: | Line 8: | ||
[[File:table io analysis.png]] |
[[File:table io analysis.png]] |
||
= Multiplier effects = |
== Multiplier effects == |
||
The multipliers of the input-output model provide an indication of what the indirect and induced effects are of an extra unit of expenditure (the direct impact). |
The multipliers of the input-output model provide an indication of what the indirect and induced effects are of an extra unit of expenditure (the direct impact). |
||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
* Type I: is the multiplier of the indirect effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro leads to an additional 0.5 million euro of indirect production, the type I multiplier is 1.5; |
* Type I: is the multiplier of the indirect effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro leads to an additional 0.5 million euro of indirect production, the type I multiplier is 1.5; |
||
* Type II: is the multiplier of the induced effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro generates an additional consumption spending by employees of 250.000 euro, the type II multiplier is 1.25. |
* Type II: is the multiplier of the induced effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro generates an additional consumption spending by employees of 250.000 euro, the type II multiplier is 1.25. |
||
== References == |
|||
<references /> |
|||
= MAP = |
|||
<websiteFrame> |
|||
website=http://securipedia.tno.nl/cool/index.php?wiki=securipedia.tno.nl&concept=Input/output-analysis |
|||
height=1023 |
|||
width=100% |
|||
border=0 |
|||
scroll=auto |
|||
align=middle |
|||
</websiteFrame> |
|||
<headertabs/> |
|||
Revision as of 09:58, 16 March 2012
Input/output analysis
An input-output model is a quantitative economic technique that captures inter-industry transactions. It is based on the idea that outputs from one sector in the economy become the inputs to another. For example, in order to build houses, a construction company will buy building materials from suppliers. The technique of Input-output analysis is originally created by Wassily Leontief (1965).
Input-output table
Based on the urban development plan an Input-output table is created(see figure below). This table is used to calculate the infinite circulation of capital through inter-industry transactions (indirect effects) and internalizing the wages and transactions of households (induced effects). Since in each round capital flows out of the system (taxes, import and wages), the impact becomes gradually smaller and tends to zero in the end. This results in the so-called Leontief multipliers.
Table: Concept of an input-output model
Multiplier effects
The multipliers of the input-output model provide an indication of what the indirect and induced effects are of an extra unit of expenditure (the direct impact).
There are two main types of multipliers:
- Type I: is the multiplier of the indirect effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro leads to an additional 0.5 million euro of indirect production, the type I multiplier is 1.5;
- Type II: is the multiplier of the induced effects (compared to the direct impulse). For example, if an urban project development of 1 million euro generates an additional consumption spending by employees of 250.000 euro, the type II multiplier is 1.25.
References
MAP
<websiteFrame> website=http://securipedia.tno.nl/cool/index.php?wiki=securipedia.tno.nl&concept=Input/output-analysis height=1023 width=100% border=0 scroll=auto align=middle </websiteFrame>
<headertabs/>