Difference between revisions of "Urban Planning Process"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Development Control== |
==Development Control== |
||
Development control, or development management, is primarily concerned with the control of the use of land and property, and is the mechanism through which the objectives and policies of a city development plan is complied with. Development control refers to the planning application process and statutory provisions, and covers issues such as exempted development (i.e. development which does not require development), enforcement (with regard to unauthorised development) and other related matters. |
Development control, or development management, is primarily concerned with the control of the use of land and property, and is the mechanism through which the objectives and policies of a city development plan is complied with. Development control refers to the planning application process and statutory provisions, and covers issues such as planning consent, exempted development (i.e. development which does not require development), enforcement (with regard to unauthorised development) and other related matters. |
||
[[Image:Development Control Pre.png|800px]] |
[[Image:Development Control Pre.png|800px]] |
||
Revision as of 17:54, 1 July 2013
The urban planning process is a dual approach of development control and forward planning.
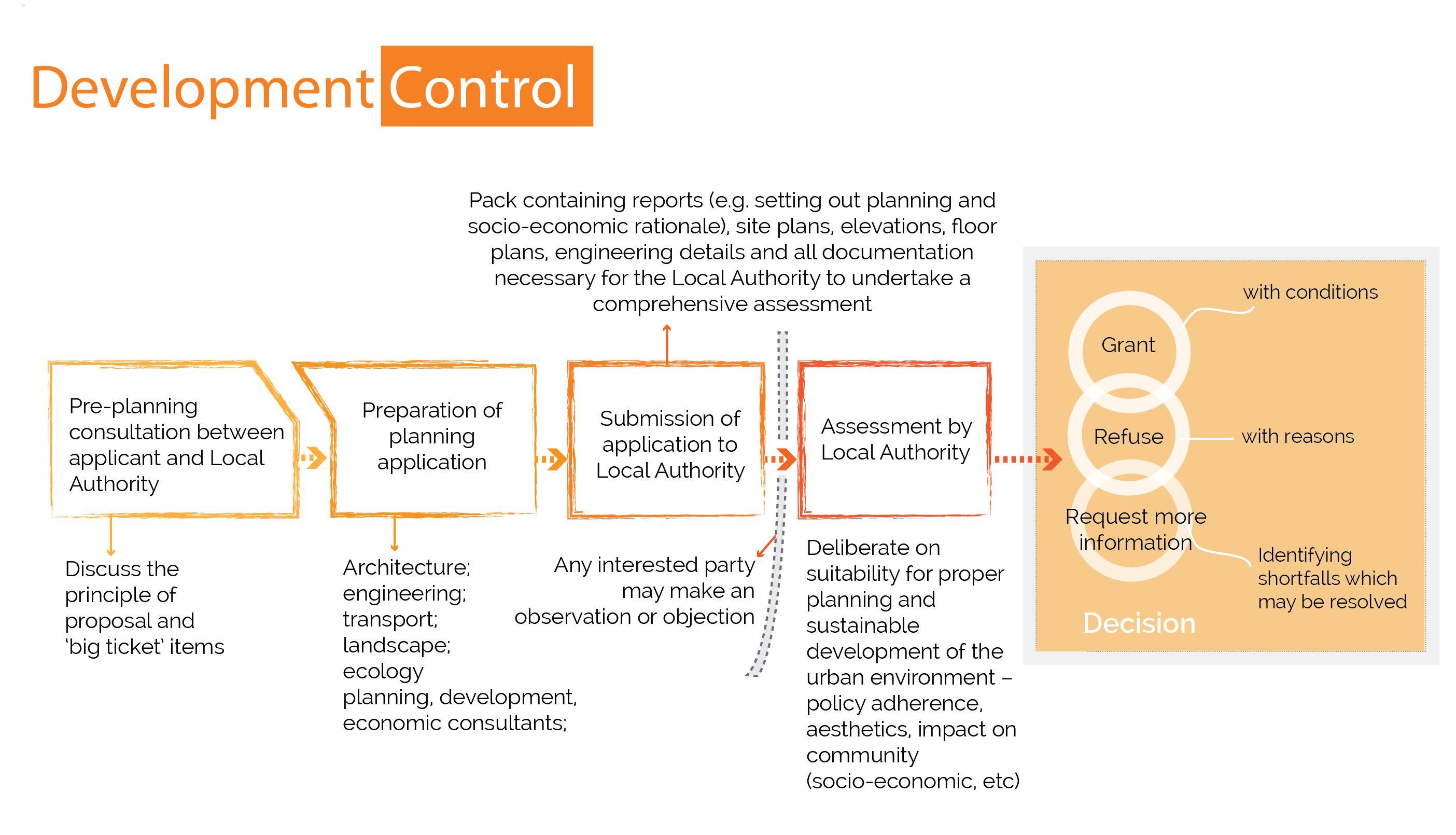
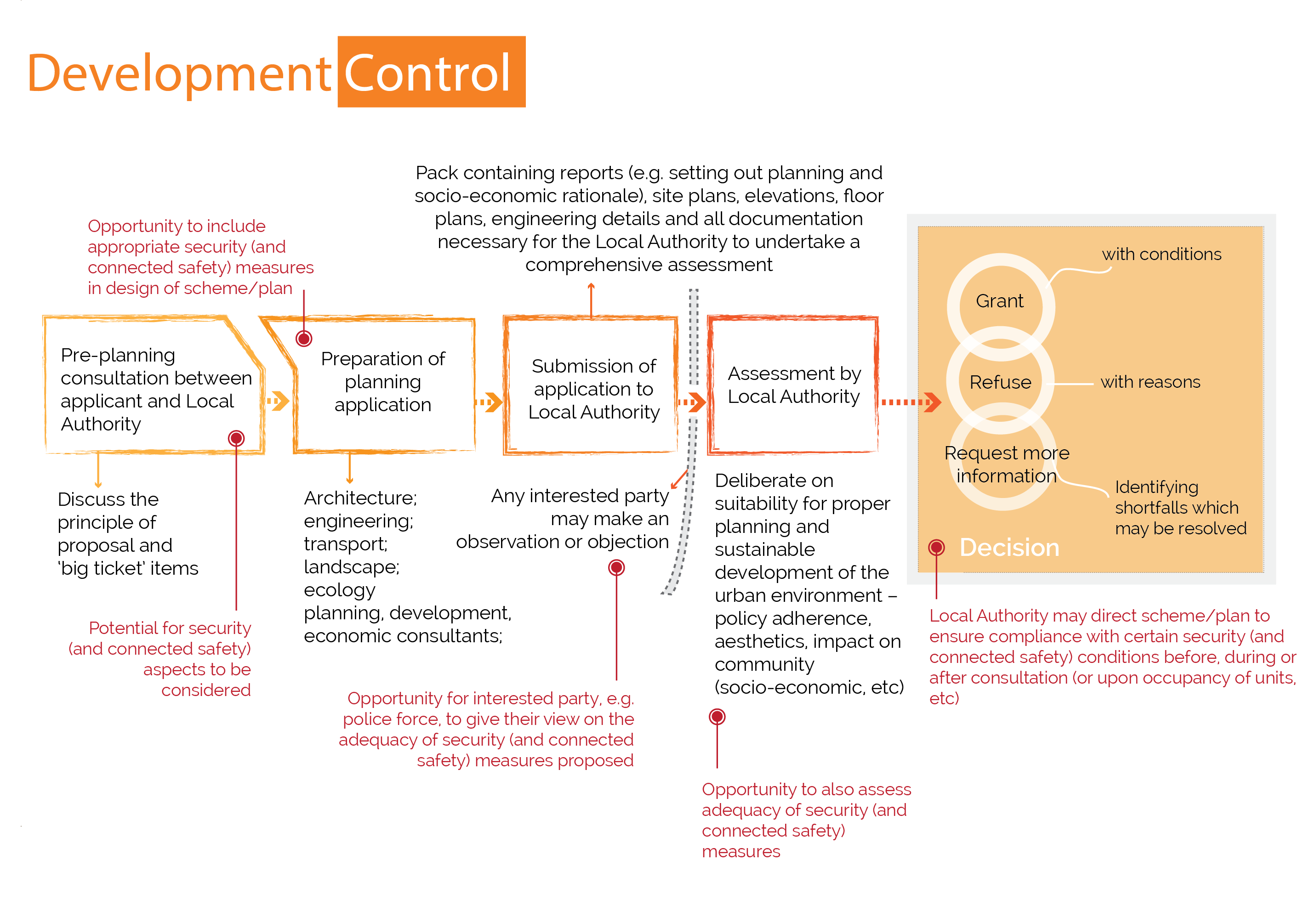
Development Control
Development control, or development management, is primarily concerned with the control of the use of land and property, and is the mechanism through which the objectives and policies of a city development plan is complied with. Development control refers to the planning application process and statutory provisions, and covers issues such as planning consent, exempted development (i.e. development which does not require development), enforcement (with regard to unauthorised development) and other related matters.
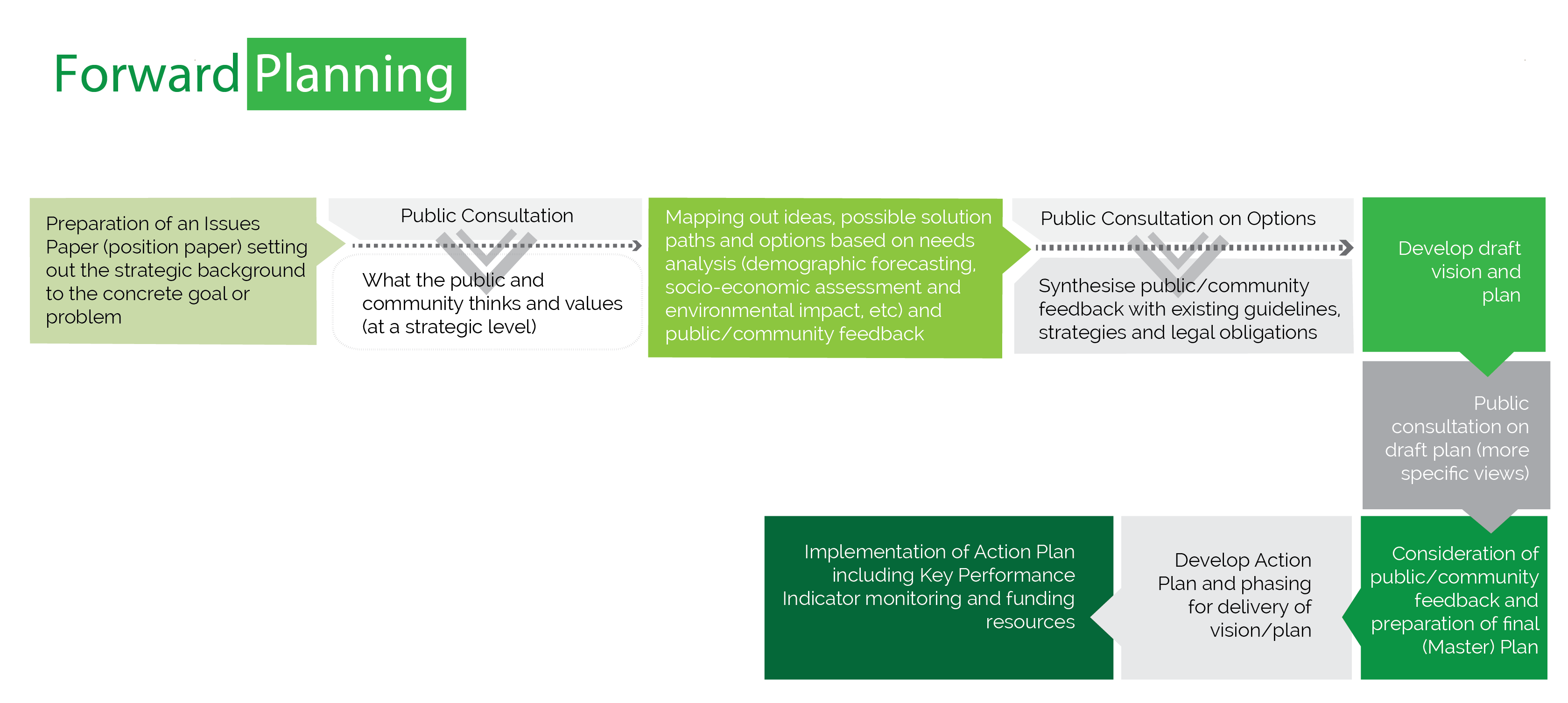
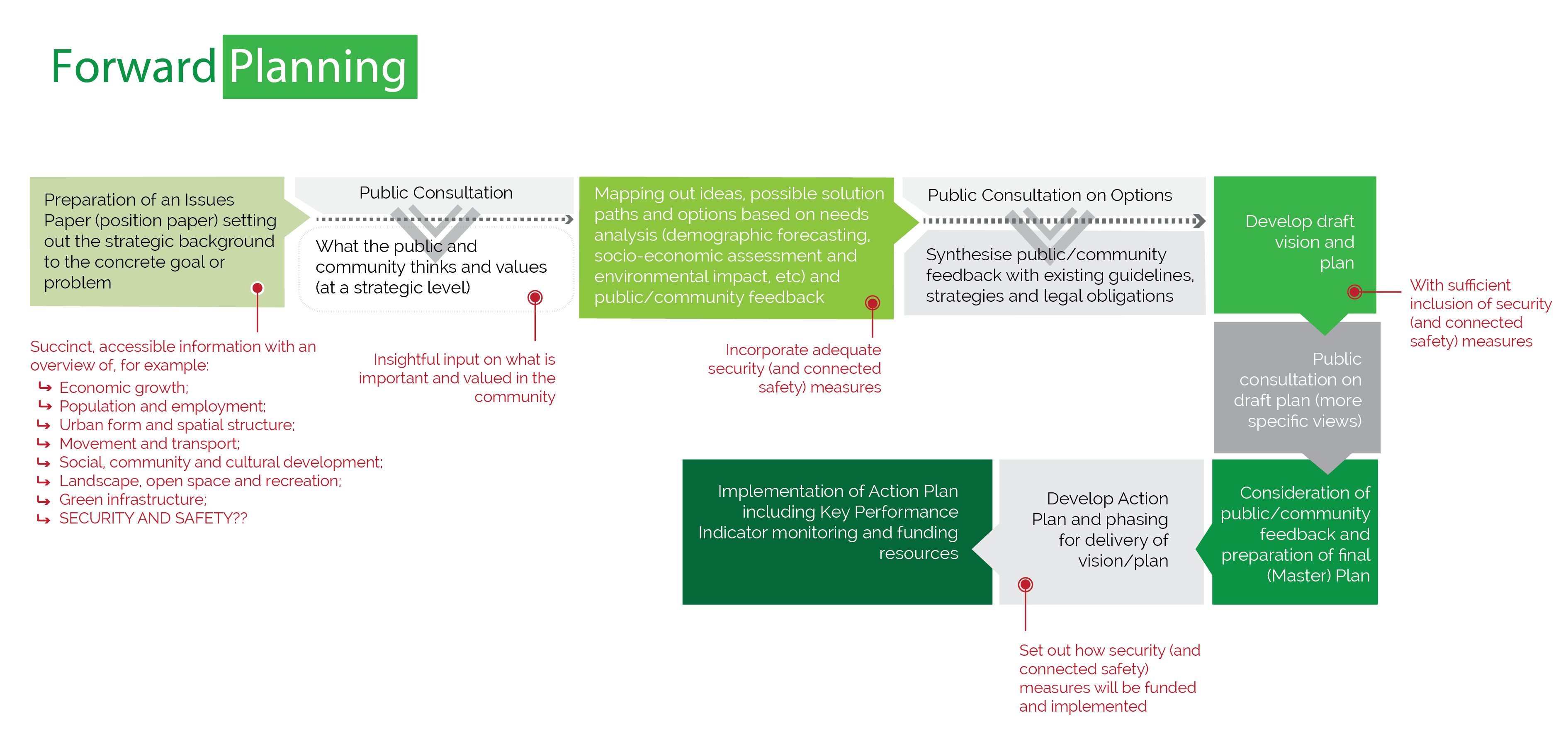
Forward Planning
Forward planning is the term used to describe the plan-making process, including a Local Area Plan for a designated regeneration quarter or for part of a city. It concerns planning for the future and designing strategies to help cities and urban areas to develop in a coordinated and coherent manner, with the necessary capacity to meet the challenges of the future. Forward planning involves identifying the strengths, constraints, opportunities and threats of an area, formulating a strategic vision, objectives and policies, and implementing a plan that is flexible and dynamic, and addresses the social, economic and technical systems in infrastructure needed for sustainable development.
Footnotes and references