Difference between revisions of "Health facilities"
| (38 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Urban object]] |
[[Category:Urban object]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
= {{PAGENAME}} = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
== Description == |
== Description == |
||
Health infrastructure can occur in varying sizes and levels of intensity, often dependent upon the primary focus of the infrastructure. They can range in size from small health centres, designed to serve a small community or residential areas up to large |
Health infrastructure can occur in varying sizes and levels of intensity, often dependent upon the primary focus of the infrastructure. They can range in size from small health centres, designed to serve a small community or residential areas up to large general hospitals which cover large urban areas. At various levels, healthcare provision is often a contentious issue, and this includes the urban planning sphere. At the micro level, the interior design of a health care facility is carefully considered. This includes the quality of the hospital room, its safety, and the relationship between nurses and patients. The meso level relates to the design of the building as a whole, the relationship of that building to the community - whether a medical complex or a surrounding neighborhood - and then, at the macro level, the design of communities for the health of their residents<ref>'Health Designers Harness Urban Planning' - Interview with Elizabeth Plater-Zyberk and Joanna Lombard (2010) 'Health Progress' . In: Journal of the Catholic Health Association of the United States. Available at: www.chausa.org. Accessed on 11 March 2013.</ref>. |
||
== Functions == |
== Functions == |
||
=== Social === |
=== Social === |
||
The key social functions of health infrastructure is in the provision of health care to those who require it. Since this involves a feeling of dependence, citizens' [[Risk_perception_mechanisms|perception of risks]] to health-related infrastructure may be substantially above professional vulnerability assessments. This should be considered in urban planning, and risk/vulnerability assessment methods applied should include [[citizen participation]]-based methods in order to address [[Public_services_and_facilities#Social|social aspects of built infrastructure dedicated to public services and facilities]]. |
|||
The key social functions of health infrastructure is in the provision of health care to those who require it. |
|||
=== Economic === |
=== Economic === |
||
The |
The economic function of health infrastructure is to ensure the health of the population and workforce. Moreover, health infrastructure creates direct employment ([[economic impact]]) to health care professionals of all levels of education<ref>Especially in smaller cities, health infrastructure belongs to the largest local employers.</ref>. As a [[Secondary economic impact|secondary economic impact]], health infrastructure creates jobs and income by purchasing goods and services from other supplying businesses and organisations. |
||
The impact of security threats is primarily crime related (e.g. burglary, theft of medicine, violence and aggression against patients and employees). Crime generates costs in anticipation of crime (e.g. locks, surveillance, etc.), as a consequence of crime (loss of property) and in response to crime (police investigation, legal system, etc.). |
The impact of security threats is primarily crime related (e.g. burglary, theft of medicine, violence and aggression against patients and employees). Crime generates [[Economic effects of crime|costs]] in anticipation of crime (e.g. locks, surveillance, etc.), as a consequence of crime (loss of property), and in response to crime (police investigation, costs of the legal system, etc.). |
||
Apart from the more traditional security measures such as policing, alarm systems, surveillance and regulatory bodies, the ‘[[Designing out approach|designing out]]’ or '[[Sustainable design|sustainable design]]' approach in the earliest stages in the planning process can be an effective measure from an economic point of view to prevent security threats and reduce the economic damage<ref>In general, these measures demand larger investments than traditional security measures, but at the same time they are able to avoid future costs due to the long-term prevention of crime.</ref>. Keep in mind, however, that also security measures create both positive and negative [[Economic effects of anti-crime security measures|economic effects]]. |
|||
=== Mobility === |
=== Mobility === |
||
The mobility associated with the different health infrastructure facilities will vary significantly depending on the type of facility, its location, the availability of public transportation modes and the patient population. |
The mobility associated with the different health infrastructure facilities will vary significantly depending on the type of facility, its location, the availability of public transportation modes and the patient population. |
||
Usually health facilities will need good [[Accessibility|accessibility]] and therefore will be located at places with good public transportation, good and well connected road infrastructure and car parking options. |
|||
=== Safety === |
=== Safety === |
||
Health |
Health facilities contribute directly to the safety, welfare and well-being of people. Disruption of these services can result in unsafe situations, as people in emergency situations would not receive required help. |
||
In general, safety functions associated with health facilities include the usual functions such as: |
|||
=== Security Issues === |
|||
* shelter from the environment (weather) |
|||
The security risks associated with health infrastructure are also dependent on the size and role of the particular piece of infrastructure. The risk of theft is always present, especially of medicines which may hold black market value, and this risk is ever present in all types and sizes of health infrastructure, especially in urban areas. Hospitals and other in-patient treatment facilities also have inherent risks associated with weak, recuperating or elderly patients that may be vulnerable to attacks, from visitors, other patients or even staff. Another important security consideration, relevant in the wake of a serious event, is the possibility of danger arising out of large volumes of people converging on a hospital seeking medical attention or in search of injured relatives. |
|||
* prevention and repression of incidents (fires, floods, air quality, etcetera) |
|||
* constructional safety (including the dynamic stresses that large crowds can exert) |
|||
* facilities to assure a timely retreat to a safe environment for the people present in case of incidents ([[Evacuation Management]]). |
|||
== Security Issues == |
|||
Policing, alarm systems, private security... |
|||
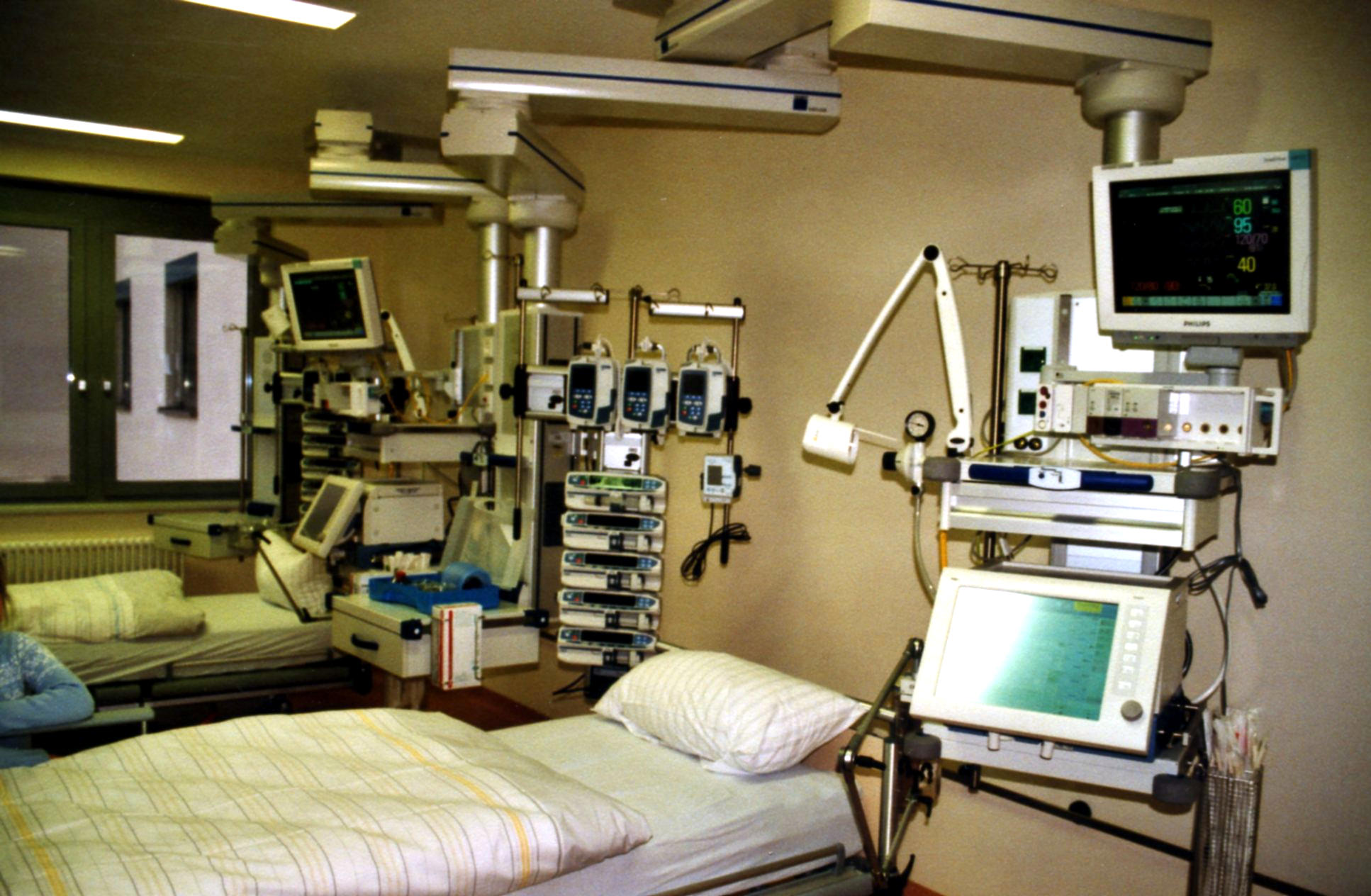
* [[image:Intensivstation (01) 2007-03-03.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Intensive care unit with expensive equipment]][[Security issue: Burglary|Burglary]]: the risk of theft is always present, especially of medicines which may hold black market value, and this risk is ever present in all types and sizes of health infrastructure, especially in urban areas. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Security issue: Assault|Physical assault]]: hospitals and other in-patient treatment facilities also have inherent risks associated with weak, recuperating or elderly patients that may be vulnerable to attacks, from visitors, other patients or even staff. |
|||
* [[Security issue: Mass killing|Mass killing]] and the associated [[Security issue: Destruction by fanatics|destruction of property by fanatics]] can be another security consideration relevant in areas with strong (ethnic) conflicts, as large volumes of people can be converging on a hospital seeking medical attention or in search of injured relatives, which not only leads to safety risks such as people getting oppressed in the crows, but also provides another attractive target for mass killing. |
|||
== Measures == |
|||
The measures for each type of security issue can be found on the respective pages. There are few measures that are generally suited or unsuited to this kind of urban object, but some specific considerations can be mentioned: |
|||
*[[Measure: Access control|Access control]] and [[Measure: Screening|screening]] generally involve a delay, which can be unsuited to the provision of emergency medical help. Health facilities are generally very public, which makes measures that restrict access less suited. The zoning (and access control) of the space within health facilities, assisted by a clear [[Measure: Directing traffic flows|direction of traffic flows]] can strongly help to reduce improper access to drugs and equipment. |
|||
General properties: |
|||
* Health facilities provide a service to the public and are therefore generally meant to be inviting, which makes very visible and impressive measures less suited. |
|||
* Health facilities know a clear distinction between staff, patients and visitors. These groups can be seperately addressed in measures like access control, direction of traffic, screening, and the level of target hardening can be tuned to the types of traffic in a particular area. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
= MAP = |
|||
<websiteFrame> |
|||
website=http://securipedia.eu/cool/index.php?concept=Health facilities |
|||
width=100% |
|||
border=0 |
|||
scroll=auto |
|||
align=middle |
|||
</websiteFrame> |
|||
<headertabs/> |
|||
Latest revision as of 15:45, 13 November 2013
Health Facilities are public services and facilities designed to provide medical care to the public.
Contents
Description
Health infrastructure can occur in varying sizes and levels of intensity, often dependent upon the primary focus of the infrastructure. They can range in size from small health centres, designed to serve a small community or residential areas up to large general hospitals which cover large urban areas. At various levels, healthcare provision is often a contentious issue, and this includes the urban planning sphere. At the micro level, the interior design of a health care facility is carefully considered. This includes the quality of the hospital room, its safety, and the relationship between nurses and patients. The meso level relates to the design of the building as a whole, the relationship of that building to the community - whether a medical complex or a surrounding neighborhood - and then, at the macro level, the design of communities for the health of their residents[1].
Functions
Social
The key social functions of health infrastructure is in the provision of health care to those who require it. Since this involves a feeling of dependence, citizens' perception of risks to health-related infrastructure may be substantially above professional vulnerability assessments. This should be considered in urban planning, and risk/vulnerability assessment methods applied should include citizen participation-based methods in order to address social aspects of built infrastructure dedicated to public services and facilities.
Economic
The economic function of health infrastructure is to ensure the health of the population and workforce. Moreover, health infrastructure creates direct employment (economic impact) to health care professionals of all levels of education[2]. As a secondary economic impact, health infrastructure creates jobs and income by purchasing goods and services from other supplying businesses and organisations.
The impact of security threats is primarily crime related (e.g. burglary, theft of medicine, violence and aggression against patients and employees). Crime generates costs in anticipation of crime (e.g. locks, surveillance, etc.), as a consequence of crime (loss of property), and in response to crime (police investigation, costs of the legal system, etc.).
Apart from the more traditional security measures such as policing, alarm systems, surveillance and regulatory bodies, the ‘designing out’ or 'sustainable design' approach in the earliest stages in the planning process can be an effective measure from an economic point of view to prevent security threats and reduce the economic damage[3]. Keep in mind, however, that also security measures create both positive and negative economic effects.
Mobility
The mobility associated with the different health infrastructure facilities will vary significantly depending on the type of facility, its location, the availability of public transportation modes and the patient population.
Usually health facilities will need good accessibility and therefore will be located at places with good public transportation, good and well connected road infrastructure and car parking options.
Safety
Health facilities contribute directly to the safety, welfare and well-being of people. Disruption of these services can result in unsafe situations, as people in emergency situations would not receive required help.
In general, safety functions associated with health facilities include the usual functions such as:
- shelter from the environment (weather)
- prevention and repression of incidents (fires, floods, air quality, etcetera)
- constructional safety (including the dynamic stresses that large crowds can exert)
- facilities to assure a timely retreat to a safe environment for the people present in case of incidents (Evacuation Management).
Security Issues
- Burglary: the risk of theft is always present, especially of medicines which may hold black market value, and this risk is ever present in all types and sizes of health infrastructure, especially in urban areas.
- Physical assault: hospitals and other in-patient treatment facilities also have inherent risks associated with weak, recuperating or elderly patients that may be vulnerable to attacks, from visitors, other patients or even staff.
- Mass killing and the associated destruction of property by fanatics can be another security consideration relevant in areas with strong (ethnic) conflicts, as large volumes of people can be converging on a hospital seeking medical attention or in search of injured relatives, which not only leads to safety risks such as people getting oppressed in the crows, but also provides another attractive target for mass killing.
Measures
The measures for each type of security issue can be found on the respective pages. There are few measures that are generally suited or unsuited to this kind of urban object, but some specific considerations can be mentioned:
- Access control and screening generally involve a delay, which can be unsuited to the provision of emergency medical help. Health facilities are generally very public, which makes measures that restrict access less suited. The zoning (and access control) of the space within health facilities, assisted by a clear direction of traffic flows can strongly help to reduce improper access to drugs and equipment.
General properties:
- Health facilities provide a service to the public and are therefore generally meant to be inviting, which makes very visible and impressive measures less suited.
- Health facilities know a clear distinction between staff, patients and visitors. These groups can be seperately addressed in measures like access control, direction of traffic, screening, and the level of target hardening can be tuned to the types of traffic in a particular area.
Footnotes and references
- ↑ 'Health Designers Harness Urban Planning' - Interview with Elizabeth Plater-Zyberk and Joanna Lombard (2010) 'Health Progress' . In: Journal of the Catholic Health Association of the United States. Available at: www.chausa.org. Accessed on 11 March 2013.
- ↑ Especially in smaller cities, health infrastructure belongs to the largest local employers.
- ↑ In general, these measures demand larger investments than traditional security measures, but at the same time they are able to avoid future costs due to the long-term prevention of crime.