Difference between revisions of "Proper planning and sustainable development"
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:ae.png|25px|right|This is a page providing background in a specific field of expertise]] |
|||
= Proper planning and sustainable development = |
|||
| ⚫ | The proper planning and sustainable development of an urban area is based on the application of evidence-based decision-making processes that result in the best actions for the urban area, its population/citizens and its environs. These actions should improve the long-term social, environmental and economic health of urban areas, including more sustainable travel patterns (modal shift towards public transport), efficient land use (appropriate densities in urban centres), good quality housing and living environments for citizens, and the protection and enhancement of natural systems. |
||
| ⚫ | The proper planning and sustainable development of an urban area is based on the application of evidence-based decision-making processes that result in the best actions for the urban area and its environs. These actions should improve the long-term social, environmental and economic health of urban areas, including more sustainable travel patterns (modal shift towards public transport), efficient land use (appropriate densities in urban centres), good quality housing and living environments for citizens, and the protection and enhancement of natural systems |
||
== Principles of sustainable development == |
== Principles of sustainable development == |
||
The principles of sustainable development largely fall under the following themes: |
The principles of sustainable development largely fall under the following themes: |
||
* Satisfaction of human needs by the efficient use of resources |
* Satisfaction of human needs by the efficient use of resources |
||
* Equity between generations |
* Equity between generations |
||
* Respect for ecological integrity and biodiversity |
* Respect for ecological integrity and biodiversity |
||
* Equity between countries and regions |
* Equity between countries and regions |
||
* Social equity |
* Social equity |
||
* Respect for cultural heritage/diversity |
* Respect for cultural heritage/diversity |
||
* Good decision-making<ref>COMHAR (Ireland) National Sustainable Development Partnership http://www.comharsdc.ie/_files/S.D.Principles.pdf</ref> |
* Good decision-making<ref>COMHAR (Ireland) National Sustainable Development Partnership http://www.comharsdc.ie/_files/S.D.Principles.pdf</ref> |
||
== Rebalancing 'sustainable' development == |
== Rebalancing 'sustainable' development == |
||
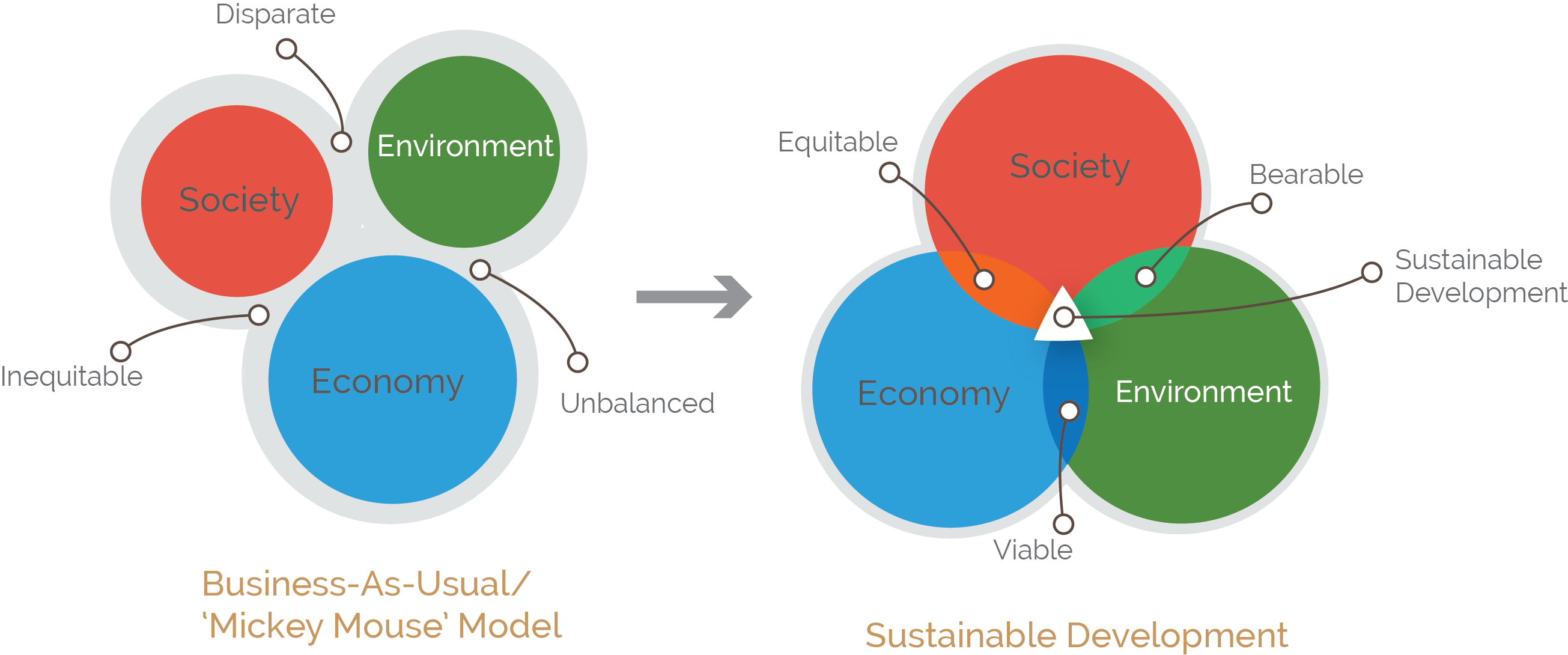
| ⚫ | Proper urban planning practices are the mechanism by which better and more informed decision making can be achieved. Traditionally, there has been an inequitable and unbalanced consideration of societal, economic and environment factors in urban areas. A renewed, more ‘sustainable’ development paradigm is now more commonly acknowledged as central to the delivery of a efficient and effective urban area. This implies a convergence between the three pillars of economic development, social equity and environmental protection. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Proper urban planning practices are the mechanism by which better and more informed decision making can be achieved. Traditionally, there has been an inequitable and unbalanced consideration of societal, economic and environment factors in urban areas. A renewed, more ‘sustainable’ |
||
<gallery> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
</gallery> |
|||
== Security (and safety) in sustainable development == |
== Security (and safety) in sustainable development == |
||
| ⚫ | With regard to security and safety in the urban area, the ‘quality of life’ of citizens, the wider functioning of the urban environment and the inter-relationship between objects within this environment will all be impacted by these considerations. Accordingly, proper urban planning and sustainable development should adequately consider security and safety in urban areas, thereby making them more resilient to potential threats and challenges posed by terrorism, organised crime and natural disasters. |
||
The importance of sustainable design in the process is explored further [[Sustainable design|here]]. |
|||
| ⚫ | With regard to security and safety in the urban area, the ‘quality of life’ of citizens, the wider functioning of the urban environment and the |
||
MORE... |
|||
{{references}} |
{{references}} |
||
= MAP = |
|||
<websiteFrame> |
|||
website=http://securipedia.eu/cool/index.php?concept=<replace with pagename> |
|||
width=100% |
|||
border=0 |
|||
scroll=auto |
|||
align=middle |
|||
</websiteFrame> |
|||
<headertabs/> |
|||
Latest revision as of 10:04, 2 January 2014
The proper planning and sustainable development of an urban area is based on the application of evidence-based decision-making processes that result in the best actions for the urban area, its population/citizens and its environs. These actions should improve the long-term social, environmental and economic health of urban areas, including more sustainable travel patterns (modal shift towards public transport), efficient land use (appropriate densities in urban centres), good quality housing and living environments for citizens, and the protection and enhancement of natural systems.
Contents
Principles of sustainable development
The principles of sustainable development largely fall under the following themes:
- Satisfaction of human needs by the efficient use of resources
- Equity between generations
- Respect for ecological integrity and biodiversity
- Equity between countries and regions
- Social equity
- Respect for cultural heritage/diversity
- Good decision-making[1]
Rebalancing 'sustainable' development
Proper urban planning practices are the mechanism by which better and more informed decision making can be achieved. Traditionally, there has been an inequitable and unbalanced consideration of societal, economic and environment factors in urban areas. A renewed, more ‘sustainable’ development paradigm is now more commonly acknowledged as central to the delivery of a efficient and effective urban area. This implies a convergence between the three pillars of economic development, social equity and environmental protection.
Security (and safety) in sustainable development
With regard to security and safety in the urban area, the ‘quality of life’ of citizens, the wider functioning of the urban environment and the inter-relationship between objects within this environment will all be impacted by these considerations. Accordingly, proper urban planning and sustainable development should adequately consider security and safety in urban areas, thereby making them more resilient to potential threats and challenges posed by terrorism, organised crime and natural disasters.
The importance of sustainable design in the process is explored further here.
Footnotes and references
- ↑ COMHAR (Ireland) National Sustainable Development Partnership http://www.comharsdc.ie/_files/S.D.Principles.pdf